Furniture Carpet Beetles Identification Guide
Anthrenus flavipes
The furniture carpet beetle is a common fabric pest that causes significant damage to upholstered furniture, carpets, and natural fiber materials. Its larvae feed on wool, silk, leather, and other animal-based materials.
Taxonomy

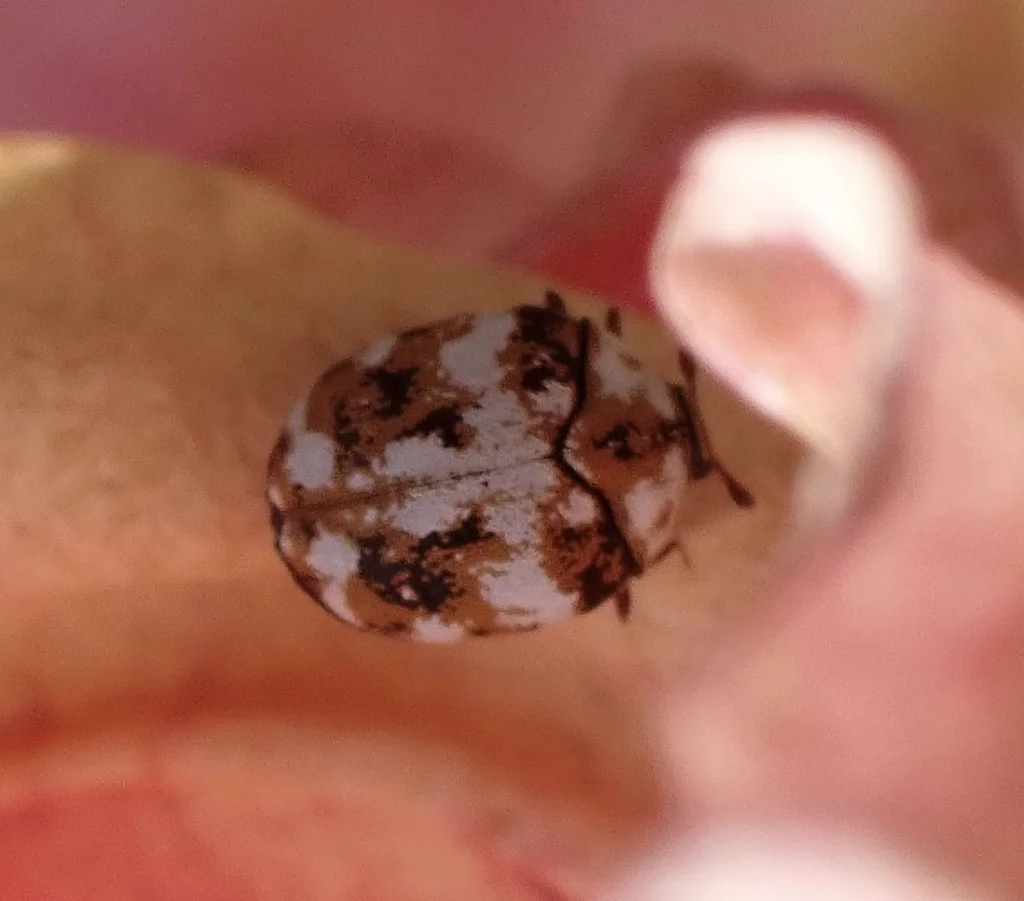
Furniture Carpet Beetles Coloration
Common color patterns to help identify furniture carpet beetles
Furniture Carpet Beetles
Seasonal Activity
When furniture carpet beetles are most active throughout the year
Where Furniture Carpet Beetles Are Found
Hover over states to see their names. Green regions indicate where furniture carpet beetles have been reported.
Furniture Carpet Beetle Identification Guide
Physical Characteristics
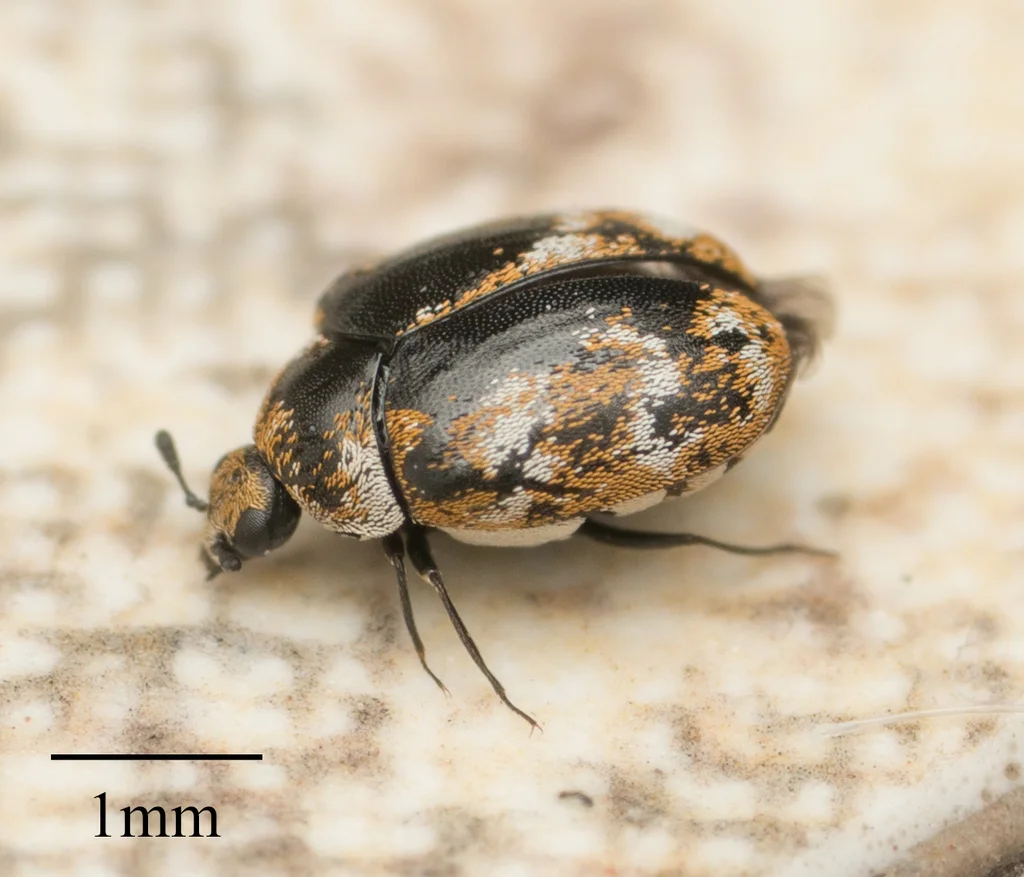
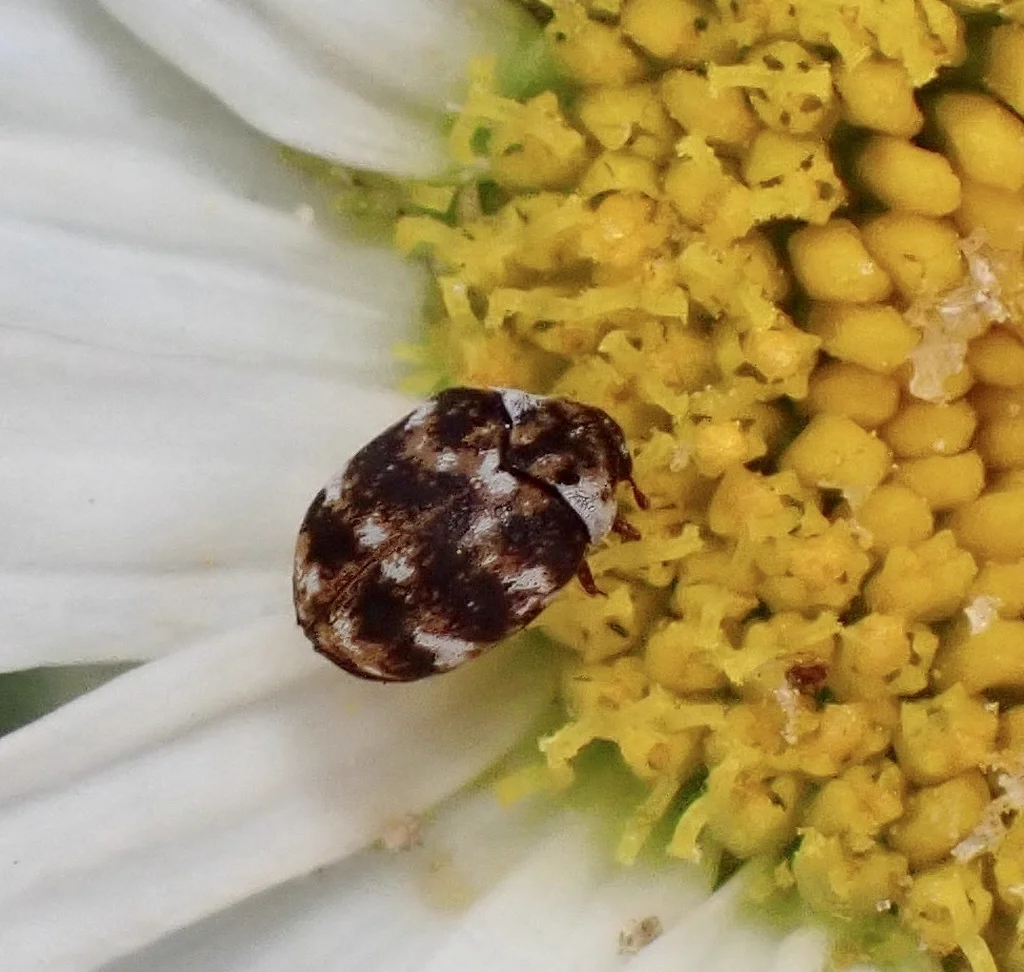
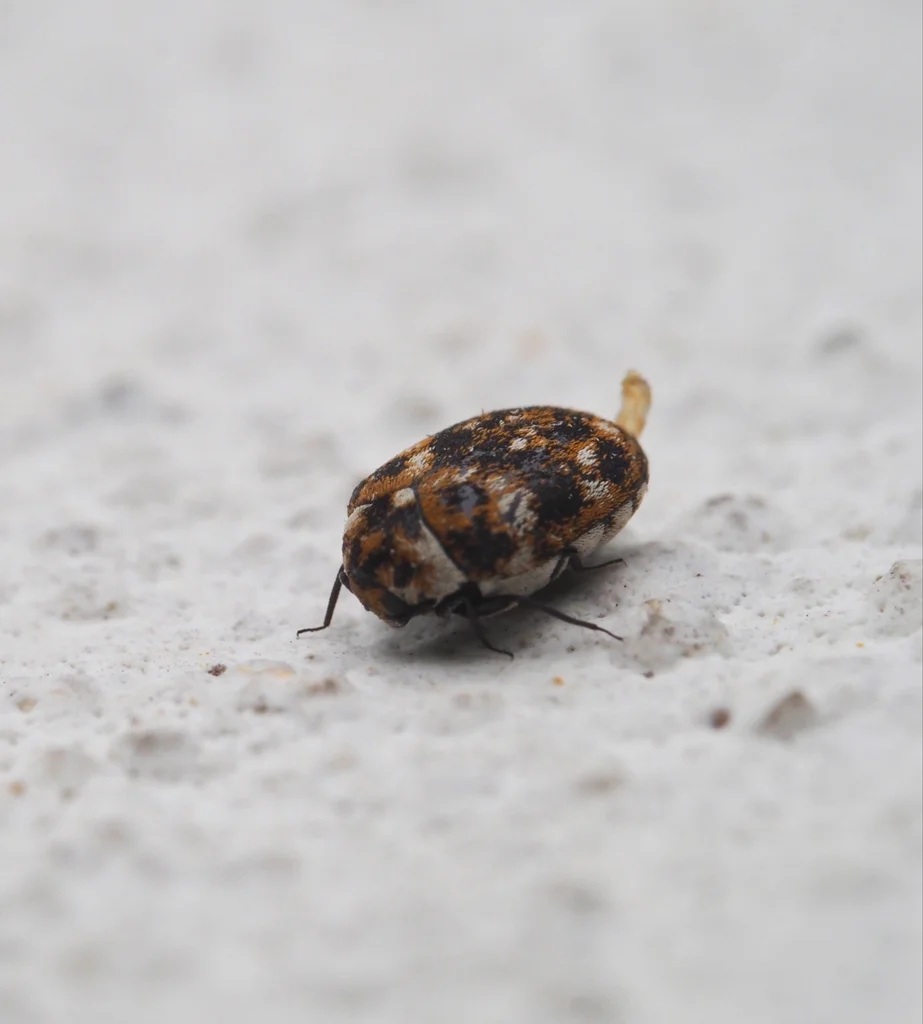
The furniture carpet beetle (Anthrenus flavipes) is a small, round insect and a common species within the carpet beetle family. It often infests couches and chairs in homes. Adults are 2 to 4mm long. Their bodies have tiny scales that make a yellow, white, and black speckled pattern.
These beetles are rounder than other carpet beetles. Their undersides are white. From above, you may see a small V-shaped notch where the wing covers meet at the back. This notch helps tell them apart from varied carpet beetles.
As beetles age, their scales can wear off. Older beetles may look solid black or dark brown. Fresh beetles show the clearest colors. Adults have short antennae and six legs. They can fly, but not well.
Larval Appearance
The larvae cause all the damage in your home. They look very different from adult beetles. Larvae are oval, about 5mm long, and covered in brown bristly hairs. They are wider at the front and thinner at the back.
The most unique feature is a tuft of long hairs at the tail end. This bundle of hairs vibrates all the time. Scientists think this helps scare away predators. All larval stages have this tuft. The number of hairs grows as the larva gets bigger.
Larvae start out white. They darken to reddish-brown as they mature. They shed their skins many times as they grow. Finding these fuzzy, brown skins is often the first sign of a problem. Learn more about identifying carpet beetle larvae and the damage they cause.
Similar Species
Varied Carpet Beetle (Anthrenus verbasci) is the most common carpet beetle. Adults have patches of white, brown, and yellow scales. They are slightly longer and less round than furniture carpet beetles.
Black Carpet Beetle (Attagenus unicolor) adults are solid dark brown to black. They are larger at 3 to 5mm. Their larvae have a single golden tuft of hairs at the tail.
Common Carpet Beetle (Anthrenus scrophulariae) is similar in size. It has clearer bands of red, white, and black scales. Its pattern is more orderly than the furniture carpet beetle.
Furniture Carpet Beetle Behavior and Biology
Life Cycle
Furniture carpet beetles go through four life stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. The full cycle takes 4 to 12 months based on temperature and food quality.
Eggs: Females lay 35 to 100 tiny white eggs in dark, hidden spots near food. Good spots include cracks in furniture, carpet edges, and areas with lint or hair. Eggs hatch in 9 to 16 days.
Larvae: This stage does all the damage. Larvae feed for 2 to 3 months before changing to pupae. In poor conditions, this can take up to a year. They shed their skins 6 to 12 times as they grow. Each shed skin is a bristly brown shell. Larvae like dark, quiet areas. They burrow into materials as they feed.
Pupae: Larvae change to pupae inside their last shed skin. Pupae are white and stay near the food source. This stage lasts 2 to 3 weeks. Pupae resist many pesticides. This is why follow-up treatments matter.
Adults: Adult beetles live 30 to 60 days. They do not damage items in your home. Instead, they feed on flower pollen outdoors. They like plants in the parsley family such as carrot, dill, and Queen Anne’s lace. Their main job is to mate and find places to lay eggs. A related species, Dermestid Beetles, shares similar characteristics.
What They Eat A related species, June Bugs, shares similar characteristics.
Furniture carpet beetle larvae can digest keratin. This protein is found in many animal-based materials: A related species, False Powderpost Beetles, shares similar characteristics.
- Upholstered furniture padding and fabric
- Wool carpets, rugs, and blankets
- Silk clothing and curtains
- Leather goods and bookbindings
- Fur coats, trim, and accessories
- Feathers in pillows and decorations
- Animal hair and pet dander
- Taxidermy and trophy mounts
- Dried insect collections A related species, Old House Borers, shares similar characteristics.
Larvae also attack plant-based and synthetic materials if they are mixed with animal fibers. Items stained with blood, feces, or animal oils draw them in. This is why dirty clothing stored without washing is at high risk.
Where They Live
Outdoors, adult furniture carpet beetles live on flowering plants. They feed on pollen from white and yellow flowers. Bird nests make great habitat since they have feathers, hair, and dead insects that larvae eat.
Indoors, these beetles have earned their name by often infesting couches and chairs. But they attack many other items too:
- Inside couches, chairs, and ottomans
- Under furniture where pet hair and lint collect
- Along carpet edges and under area rugs
- In closets storing wool or fur
- Around heating vents where debris gathers
- Inside piano felts and other fabric-lined items
- Near decorative items containing feathers or animal products
The furniture carpet beetle is most common in warmer areas. It can thrive in heated buildings anywhere in North America. Once they move in, they spread through a home by crawling along baseboards and carpet edges.
Signs of a Furniture Carpet Beetle Problem
Damage Patterns
Furniture carpet beetle damage has several telltale signs:
- Irregular holes in fabrics rather than round, uniform holes
- Surface grazing where larvae eat the nap but leave the backing intact
- Damage along seams and under cushions where larvae hide while feeding
- Worn spots on upholstered furniture, often on undersides and backs
- Damaged carpet edges where carpets meet walls or under furniture
The damage tends to stay in one area rather than scatter. Larvae stay close to their food and eat outward from where they hatched.
Warning Signs
-
Shed larval skins are brown, bristly shells found near damaged items or in corners. These pile up over time and look unique.
-
Adult beetles on windowsills are a sign of breeding indoors. They seek light and try to get outside in spring and summer.
-
Small fecal pellets are tiny particles near damaged areas. They look like sand and match the color of what larvae have been eating.
-
Larvae crawling on walls show up when older larvae wander from food sources looking for places to pupate.
-
Allergic reactions can happen. Some people get skin rashes or itching from contact with larval hairs.
How We Treat for Furniture Carpet Beetles
Good carpet beetle control requires targeting all life stages. It also means removing conditions that help them thrive.
Inspection
Our technicians begin with a thorough inspection to:
- Find the main food sources and breeding sites
- Identify all affected materials and areas
- Assess the severity of the infestation
- Look for conditions that attract beetles, such as lint buildup or poor storage
We check couches, chairs, closets, storage areas, and vents. We look anywhere with natural fibers. We also check for bird or insect nests near the home. These can be outdoor breeding sources.
Treatment Methods
Targeted Residual Applications: We apply products to cracks, crevices, carpet edges, and furniture seams where larvae travel and feed. These products keep working over time to kill newly hatched larvae.
Insect Growth Regulators (IGRs): IGRs stop larvae from growing into adults that can breed. This breaks the lifecycle. It also protects against eggs and pupae that survive the first treatment.
Dust Treatments: For wall voids, furniture frames, and other hidden areas, we use insecticidal dusts. These reach spots where larvae often grow out of sight.
What You Can Do to Help
Treatment works best when homeowners participate:
- Vacuum well to remove larvae, eggs, and debris from furniture, carpets, and baseboards
- Dry clean or hot wash fabrics since heat above 120 degrees F kills all life stages
- Store woolens right in sealed containers or garment bags
- Clean up lint and pet hair because regular cleaning removes food sources
- Check used items and inspect secondhand furniture and clothing before bringing them home
Follow-Up and Prevention
Eggs and pupae can survive the first treatment. We schedule follow-up visits 2 to 4 weeks later to kill newly hatched larvae before they cause more damage or breed.
We also share tips on storage habits, cleaning routines, and ways to make your home less inviting to carpet beetles.
References and Further Reading
Other Carpet Beetles
Explore other species in the carpet beetles family
Commonly Confused With
Furniture Carpet Beetles are often mistaken for these similar pests
Where Furniture Carpet Beetles Are Found
Hover over states to see their names. Green regions indicate where furniture carpet beetles have been reported.
Common Questions about Furniture Carpet Beetles
What does a furniture carpet beetle look like?
+
Adult furniture carpet beetles are small (2-4mm), round insects covered in tiny scales. The scales form a speckled pattern of yellow, white, and black. They are rounder than other carpet beetle types. Their undersides are white. Larvae look like fuzzy, oval grubs about 5mm long with brown hairs.
What do furniture carpet beetles eat?
+
Larvae eat natural materials like wool, silk, fur, feathers, leather, and hair. They love upholstered furniture and eat both the padding and fabric. They also feed on carpets, clothing, and items stained with food or sweat.
Are furniture carpet beetles harmful to humans?
+
Furniture carpet beetles do not bite or spread disease. However, their larval hairs can cause allergic reactions and skin irritation in some people. The main concern is damage to furniture, carpets, and clothing made from natural fibers. Read more about [whether carpet beetles are dangerous](/are-carpet-beetles-dangerous/).
How do furniture carpet beetles get into my house?
+
Adult beetles fly and are drawn to flowers for pollen. They enter through open windows, doors, or gaps around pipes. They also come in on cut flowers, used furniture, or old clothing. Once inside, females look for dark spots near natural fiber items to lay eggs.
Where do furniture carpet beetles hide?
+
Larvae prefer dark, undisturbed areas near their food sources. Check inside and under upholstered furniture, along carpet edges and baseboards, in closets with wool items, and around air vents where lint collects. Adults are often found on windowsills as they try to get outside.
How long does it take to get rid of furniture carpet beetles?
+
Treatment usually takes 2-3 months to get rid of a problem. The full lifecycle can last 4-12 months. Eggs and pupae resist many treatments. Follow-up visits are needed to kill newly hatched larvae.
How can I tell furniture carpet beetle damage from moth damage?
+
Carpet beetle damage makes irregular holes in fabrics. Moth damage looks more even with round holes. Carpet beetles also leave behind shed larval skins that look like fuzzy brown shells. You may also find small pellets near damaged areas.
With five years of hands-on experience in the pest control industry, George Schulz is a registered technician with the Virginia Pest Management Association and a proud third-generation professional in a family business that's been protecting homes for over 57 years. He manages and trains a team of service pros while also leading internal research efforts—recently spearheading a deep-dive review of thousands of documents on pest control materials to hand-pick the most kid and pet friendly, most effective solutions tailored specifically for homes in the DC metro area.