Mosquitoes can shut down your backyard fun with their itchy bites. Ever wondered how long do mosquitoes live? Knowing their life span and life cycle helps you time treatments for the best results.
Our home had a swamp of mosquitoes thanks to thick shrubs and standing water. We tried dozens of fixes until our In2Care traps plus a targeted vegetation spray broke the breeding cycle.
In this guide, we’ll cover the four stages of the mosquito life cycle, average lifespans by sex and species, seasonal peaks in the DMV, and practical control tips.
What Does “How Long Do Mosquitoes Live” Mean?
Understanding lifespan versus life cycle is key. Lifespan (or life span) means how long an adult lives. The life cycle covers all stages: egg, larva, pupa, adult. Knowing both guides your mosquito control timing. For more on mosquito biology, see our full guide on Mosquitoes.
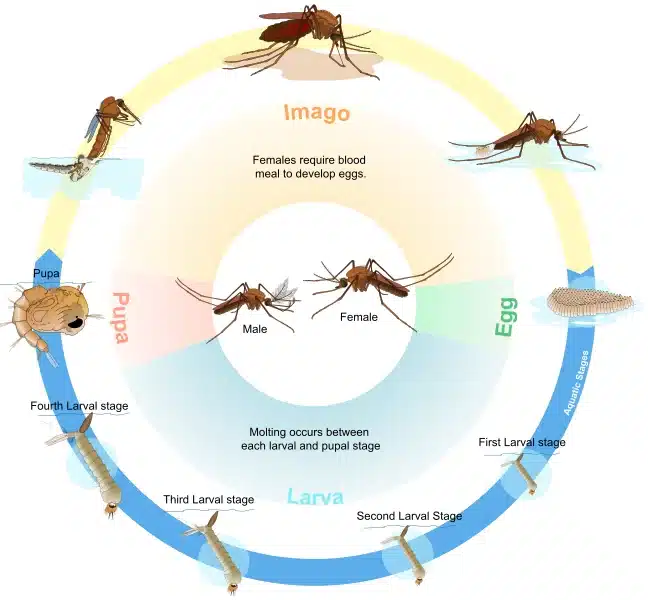
The Four Stages of the Mosquito Life Cycle
According to the CDC, all mosquitoes go through four stages before they bite.
Egg: From Mosquito Eggs to Hatch
Mosquito eggs are laid on or near water.
- Culex females lay floating rafts on stagnant water.
- Aedes females glue eggs just above the water line; they can survive dry for months before they hatch.
Larva: The Mosquito Larva Stage
Larvae, or wigglers, live in water and feed on microbes. They molt four times (go through four instars) and usually become pupae in 4-7 days if water temperature and food supply are right.
Pupa: Transition to Adult Mosquito
Pupae, called tumblers, don’t feed. They rest near the surface for 2-5 days before the adult mosquito emerges.
Adult Mosquito: Emergence and Feeding
Adult mosquitoes dry their wings and fly off.
- Female mosquitoes bite and need a blood meal to develop eggs.
- Male mosquitoes feed on nectar only and live about a week.

Average Lifespan: How Long Do Mosquitoes Live by Sex and Species
Female Mosquito Lifespan
In summer, adult female mosquitoes live about 2-4 weeks. They can lay up to three batches of eggs, about 100-300 eggs each. Under ideal lab conditions, some females can live up to 3-4 months.
Male Mosquito Lifespan
Male mosquitoes usually live 7-10 days. They do not bite; instead, they feed on nectar and pollinate flowers.
Common Mosquito Species and Their Lifespans
Aedes albopictus (Asian Tiger Mosquito)
- Egg to adult in 7-10 days in warm weather.
- Females live about 30-40 days and feed on blood and nectar.
- Eggs can stay dormant in dry containers for months.
- Known as a day biter and vector for dengue and chikungunya.
Culex pipiens (Northern House Mosquito)
- Egg-to-adult in about 1-2 weeks.
- Active females live about 2-3 weeks; some enter diapause and hibernate through winter.
- Night biters and primary carriers of West Nile virus.
Environmental Factors That Influence How Long Mosquitoes Live
Key Environmental Factors
- Temperature: Heat speeds development but shortens adult life.
- Humidity: High moisture reduces desiccation; dry air is deadly.
- Nutrition: Nectar and blood feeding extend life span.
- Predation: Birds, bats, fish, and other insects prey on mosquitoes.




Seasonality: When Mosquitoes Live in the DMV Region
Spring Onset of Mosquito Season
In the DMV, mosquitoes start appearing in April once temperatures hit about 50°F. Early yard cleanup prevents many larvae. According to Montgomery County, MD, spring source reduction is key.
Summer Peak of Mosquito Activity
From June through August, overlapping generations mean constant biting and higher West Nile virus risk. Humid, warm nights let female mosquitoes live longer and feed more often.
Autumn Decline and First Frost
Mosquito activity drops after the first hard freeze (often October to early November). Aedes eggs persist in dry sites, while Culex females hide in crawlspaces until spring.
Overwintering: How Mosquitoes Survive Winter
- Aedes eggs lie dormant in containers.
- Culex females hibernate in sheltered spots, ready to resume biting when it warms up.
How Weather and Climate Change Extend Mosquito Season
Warmer springs and milder falls are adding “mosquito days” each year. A 2024 analysis found season length in many regions may grow by 1-2 months by 2050.
Using Life Cycle Insights for Effective Mosquito Control
Target mosquitoes at vulnerable stages to break their life cycle:
- Remove standing water weekly.
- Treat water bodies with larvicides.
- Apply barrier sprays before adult peaks. Learn more in our Mosquito Control Process: Reclaim Your Backyard.
Proven Backyard Solutions: Our Family’s Fight with Mosquito Lifespan
IN2Care Mosquito Trap System
These stations lure resting mosquitoes. The gauze strips contain larvicide and a fungus that females pick up and carry to breeding sites.
Topical Spray to Vegetation
Our registered technicians use a backpack sprayer with an adulticide plus Insect Growth Regulator. They focus on shaded foliage, ivy patches, and brush lines for knockdown.
Professional Mosquito Treatments and Timing
Larviciding Best Practices
Use Bti dunks or granules in standing water every 7-10 days from April to October. This stops most larvae from completing their life cycle.
Adulticiding (Barrier Sprays and Fogging)
Spray at dusk or dawn around your yard’s ecotone. This living edge treatment knocks down adult mosquitoes resting on leaves.
Integration with Local Services
- Reston Mosquito Control
- Herndon Mosquito Control
- Alexandria Mosquito Control
- Ashburn Mosquito Control
- Sterling Mosquito Control
- Woodbridge Mosquito Control
- Frederick Pest Control

DIY Mosquito Control Tips Based on Mosquito Lifespan
Seasonal Maintenance Schedule: Targeting the Mosquito Life Cycle
Year-Round Mosquito Control Calendar
- April-May: Source reduction and larviciding.
- June-August: Barrier sprays and personal protection.
- September-October: Yard cleanup and prepare for winter.
Further Reading and Internal Links
- Male vs Female Mosquito: Why Only Females Transmit Disease
- Mosquitoes
- The Mosquito Control Process: Reclaim Your Backyard
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the lifespan of a mosquito after it bites a person?
+
After a blood meal, a female mosquito can live 2-4 more weeks as she lays her eggs. Each bite helps her produce the next batch of **mosquito eggs**.
What smell do mosquitoes hate?
+
Mosquitoes hate citrus scents like lemon eucalyptus and citronella. These **mosquito repellents** can mask the **carbon dioxide** you exhale.
How long will a mosquito live in your house?
+
An indoor mosquito without predators can live up to a few weeks if it finds nectar and moisture. Dry, cool areas shorten their **life span**.
What kills mosquitoes instantly?
+
Ultra-low-volume fogging with adulticides can knock down adult mosquitoes on contact. Electric zappers and **mosquito traps** also provide quick control.
How do mosquitoes find their hosts?
+
Mosquitoes use **carbon dioxide** and body heat to detect hosts. They also sense odors from skin and clothing.
Can mosquitoes hibernate indoors?
+
Species like Culex pipiens can **hibernate** in basements or crawlspaces. They stay dormant until spring warms up.
What affects mosquito development time?
+
Water temperature and food availability can speed up or slow down the larval stage. Warm water lets larvae **complete their life cycle** in under a week.
Are all mosquito species equal in lifespan?
+
No. **Different mosquito species** have varied lifespans. Some Aedes live 30-40 days, while others only a couple of weeks.
Do male mosquitoes bite humans?
+
Male mosquitoes only feed on nectar. They lack the **proboscis** needed to bite humans.
How can I prevent mosquito breeding?
+
Regularly dump containers with standing water, treat ponds with larvicides, and keep gutters clear. **Prevent mosquito** habitat to break the life cycle.
With five years of hands-on experience in the pest control industry, George Schulz is a registered technician with the Virginia Pest Management Association and a proud third-generation professional in a family business that's been protecting homes for over 57 years. He manages and trains a team of service pros while also leading internal research efforts—recently spearheading a deep-dive review of thousands of documents on pest control materials to hand-pick the most kid and pet friendly, most effective solutions tailored specifically for homes in the DC metro area.